| 15 min read
What is Cloud Connect?
IP connect, cloud connect, direct connect, dedicated interconnect, direct link, fast connect …... What does it all mean?!?

An introduction to cloud connectivity
Many Network Service Providers (NSP’s) have a range of options when it comes to cloud connectivity, though a lack of industry standards and confusing terminology can make things difficult to understand.
Do you know the difference between IP connect, cloud connect, direct connect, dedicated interconnect, direct link and fast connect? Is there a difference?
We enlisted the help of our cloud architects and product managers to help you cut through the noise and avoid the confusion.
The history of cloud connect
Not so long ago, the only option available to connect to a public Cloud Service Provider (CSP) was over the public internet. However, with the rapid shift to cloud computing, customers quickly began to demand more – better security, lower latency, higher throughputs and increased reliability.
CSP’s soon realised better end-to-end cloud performance wasn’t going to be possible using the public Internet. They also understood that they didn’t have the expertise or the infrastructure to manage interconnectivity between dozens of NSP’s and colocation racks in their own data centres.
CSP’s also quickly realised the answer was in the hundreds of carrier neutral data centres spread all over the world. Besides some companies already co-locating in these neutral data centers, most NSP’s were also already present at these locations, so CSP’s could extend their backbone connectivity to meet them there. This provided the potential for a direct physical link between the NSP network and the CSP network, bypassing the regular Internet and providing a pseudo-private network.
This interconnectivity, known as direct cloud connect / private connectivity, enabled direct, end-to-end fiber connectivity and brought with it a whole range of security, latency and performance improvements. In addition also cost efficiencies for customers moving high volumes of data from cloud environments to their locations.
Nowadays you will find that certain cloud connect offerings are also available in automated ways over digital infrastructure platforms to enable instant delivery to the cloud. These On Demand platforms offer a number of benefits including online ordering via a portal or API, real-time delivery of new services and bandwidth that can be scaled in minutes with flexible commercial options.
Today, cloud connectivity falls into two buckets, one that relies on the public Internet, and another that uses private, dedicated connectivity. Within these 2 buckets are typically 6 different connectivity options available.
We’ll walk you through 6 cloud connectivity options and explain the pros and cons of each, so that you can choose the most suitable cloud access solution for your needs. These are:
Cloud connectivity using public internet
Arguably the cheapest and easiest way to connect to the cloud is through your standard Internet connection over the public Internet, sometimes referred to as IP access or IP transit.
Using your public Internet access is easy to set up and versatile, as accessing the cloud is just one of the many use cases for a standard Internet access connection. It provides a cost-efficient access method where you don’t have specific performance needs and do not have to move high volumes of data from cloud environments to your location. These days you see that certain NSP’s have this offering also available in automated ways over digital infrastructure platforms which allows customers to benefit from real-time ordering, provisioning and bandwidth flexing.
However, accessing cloud applications via the public Internet can also result in performance inconsistencies and increased security risks. You can think of public Internet routes like a highway – they’re dynamic and shared which can result in congestion at times, and when the most direct link is not available, data is routed through the next best option, which you have no control over resulting in packet loss and increased latency (delays). Additionally, multiple hand-offs between ISPs creates instability in the connection and increased risk.
Essentially the more pops and routers involved in delivering your data to its final destination, the more points of potential failure and a wider surface area for security attacks. Despite this, the growth of cloud connectivity via public Internet (nowadays with automation capabilities) has shown no sign of slowing down. The public Internet remains by far the most common way to access the cloud.

Stay secure beyond borders
A guide to SASE implementation
With employees working remotely and critical systems moving to the cloud, traditional network perimeters have exploded and businesses need to stay secure beyond borders to enable success. Download the free guide to discover a guide to SASE implementation, to help you find the right pathway for your business.
2. Cloud connectivity using public internet and cloud prioritisation
Internet connectivity with cloud prioritisation enables you to dynamically reserve a portion of your normal Internet bandwidth for select cloud applications. Traffic prioritisation is effective for both incoming and outgoing traffic enabling a consistent, SLA-backed user experience specifically for your traffic to the cloud.
Cloud prioritisation is offered by NSP’s that have direct peering services with cloud providers, such as Microsoft. For example, Microsoft Azure Peering Services (MAPS for short) enables end-users direct access to Microsoft cloud services through certified network providers. Once in place, your cloud traffic stays completely on your providers network, bypassing the public Internet and avoiding any other intermediary Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
The service also enabling cloud prioritisation for Microsoft Teams, Office 365, Azure, or any other Microsoft SaaS application. It ensures traffic destined for these services takes the shortest possible path, ensuring the lowest possible latency.
Cloud prioritisation combines the benefits of optimised routing and direct peering infrastructure with traffic prioritisation over the last mile, between the customer router and provider edge.
* only available from some MAPS providers
3. Direct Ethernet cloud connect
Dedicated connectivity through Ethernet connectivity services is the fastest and safest route for cloud connectivity, and the first of the Internet-bypass solutions. Direct cloud connectivity provides the secure, high performance, end-to-end connectivity needed to run critical applications that can’t be rivalled when only using the Internet. It is the result of CSP’s like AWS, Microsoft, Google, Oracle and IBM working together with NSP’s to enhance end-to-end cloud connectivity and automation capabilities – without customer traffic touching the Internet. End-users are probably already familiar with the names of these CSP’s direct interconnect programs – like AWS Direct Connect, Microsoft ExpressRoute and Google Cloud Interconnect – that enable private end-to-end secure connectivity through a NSP towards the customer location.
Direct Ethernet connectivity to the cloud renders performance, and security problems obsolete. It helps customers to have reliable, low-latency, consistent and high throughput to the cloud. It’s provided by cloud on-ramps at neutral data centres where the public CSP’s are present. This connects your premises or facilities through a NSP to the cloud provider via a direct layer 2 link and nowadays also available in automated ways over digital infrastructure platforms to enable instant delivery to the cloud. These On Demand platforms offers a number of benefits including online ordering via a portal or API, real-time delivery of new services and bandwidth that can be scaled in minutes with flexible commercial options.
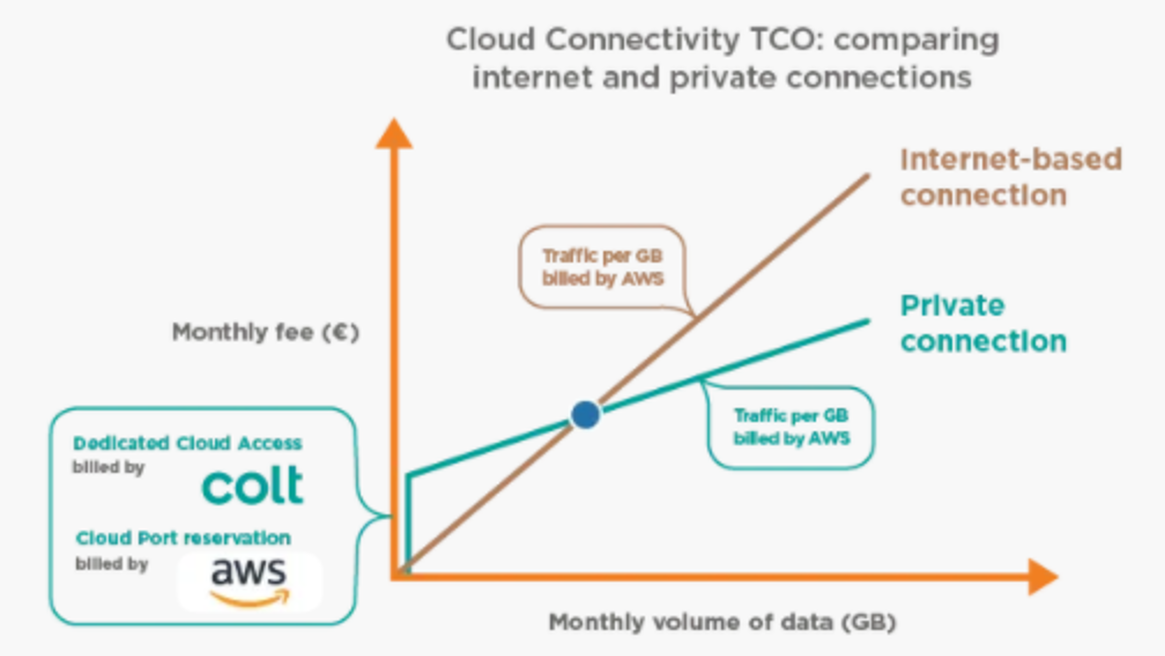
CSP’s typically charge data transfer fees – which are different when connecting to the Cloud through direct Ethernet connectivity vs. through the Internet, so direct connectivity can be particularly cost-effective if you are likely to be transporting large amounts of data out from your cloud environment (known as ‘egress’) towards your location. Below example for connecting towards AWS comparing a dedicated offering (AWS Direct Connect) vs. connecting through the Internet.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:

Stay secure beyond borders
A guide to SASE implementation
With employees working remotely and critical systems moving to the cloud, traditional network perimeters have exploded and businesses need to stay secure beyond borders to enable success. Download the free guide to discover a guide to SASE implementation, to help you find the right pathway for your business.
4. Wave cloud connect
Together with the increased demand for cloud connect, the requirement for higher bandwidths is growing. Optical cloud connect (or Wavelengths or Layer 1 connectivity) is mainly referring to the market of extreme high bandwidth connections to the Cloud. These services are delivered over Optical Layer 1 digital platforms and can deliver 10G or 100G connectivity services towards a Cloud Service Provider.
The Optical Wave services are known in the market for the end-to-end transparency on data transmission, for being fully managed and for the important features they offer such as end-to-end routing diagram with KMZ, zero frame loss & jitter and fixed latency.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
MPLS IP VPN connect
Integrating cloud connectivity into an IP-VPN (also known as IP-VPN cloud connect or MPLS-WAN technology) is a scalable and cost-effective way to access cloud services within a network.
MPLS IP-VPN provides direct, high bandwidth and secure cloud connectivity to CSP’s. It’s suited to customers that require secure access to the cloud across multiple sites and has traditionally been a common way for businesses connect to cloud providers.
The cloud connection is directly integrated into the IP-VPN, so that it is completely private, with no reliance on the Internet. The cloud locations are integrated into the private WAN and effectively seen as another site (or sites) on the IP-VPN, meaning there is no need to redesign large corporate networks. Different customer locations in the IP-VPN then share the connectivity to access their resources in the cloud.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
SD-WAN cloud connect
SD-WAN (sometimes called SD-WAN Cloud Access or SD WAN Multi-Cloud) can connect your software-defined WAN infrastructure to multiple cloud service providers (such as AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud) to enable direct, high performance and secure multi-cloud connectivity. Each branch office benefits from seamless end-to-end connectivity to your public cloud providers.
For cost-effective, direct connectivity into multiple cloud environments, SD-WAN is likely the optimal solution.
SD-WAN offers sophisticated and comprehensive connectivity capabilities, with features including prioritisation, optimisation, security, analytics, automated provisioning and deployment. It brings together a single cohesive view of the enterprise network, tying together WAN sites, IaaS/SaaS cloud, and branch site connectivity, typically all within a single online portal. Coupled with on-demand capabilities such as zero touch site provisioning and real-time bandwidth upgrades, SD-WAN is an extremely powerful solution.
Prior to SD-WAN, traffic was typically backhauled to a central site or regional hub where a physical hardware stack provided functionality that was cost prohibitive to deploy at satellite sites (such as security and analytics). SD-WAN now enables this functionality to be deployed in software on a common hardware platform. These software stacks comprise of various software functions that can be dynamically loaded and deployed in a modular fashion with a range of functionality, including:
- Networking & routing
- Analytics
- Security
- Traffic optimisation
- Remote access
- and more
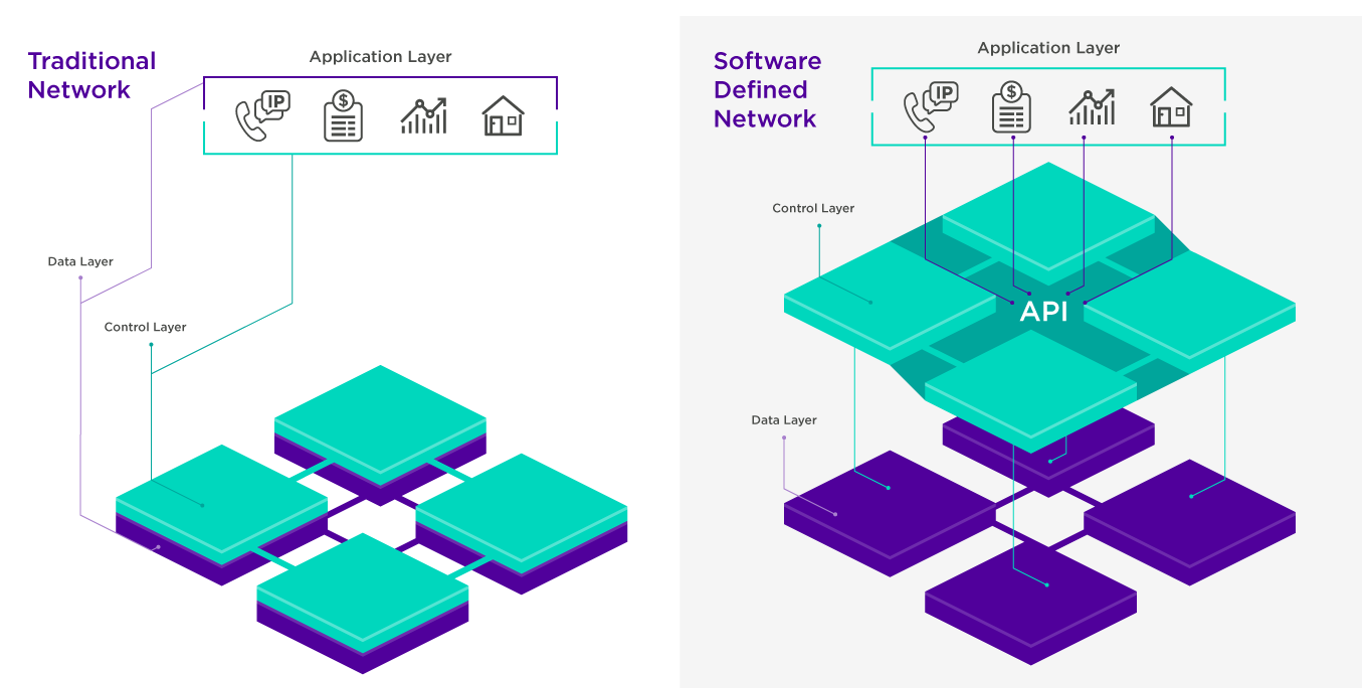
By tying together WAN sites and cloud infrastructure SD WAN can deliver end-to-end security, performance and visibility.
Building on MPLS IP VPN above, SD WAN offers private connectivity into multiple cloud providers in a single solution, combined with end-to-end performance backed by a SLA, end-to end security, and end-to-end analytics.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Questions to ask your cloud connect provider
There is no ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution for enterprises as they connect to the cloud, here are some things to consider.
Top 10 questions and considerations to ensure you remain future-proofed by a new provider:
- What level of partnership do you have with the major cloud providers?
- How many public cloud points of presence do you have?
- How many data centres are currently connected to your network?
- How many offices are currently connected to your network?
- Do you provide on demand capabilities via a self-serve software portal?
- Are you data centre and cloud service provider neutral?
- Who owns your fibre network - is it privately owned or leased from a 3rd party?
- Do you provide end-to-end connectivity, including the last mile?
- Do you provide guaranteed SLAs including for latency, packet loss and throughput?
- What bandwidths are supported for cloud connectivity?
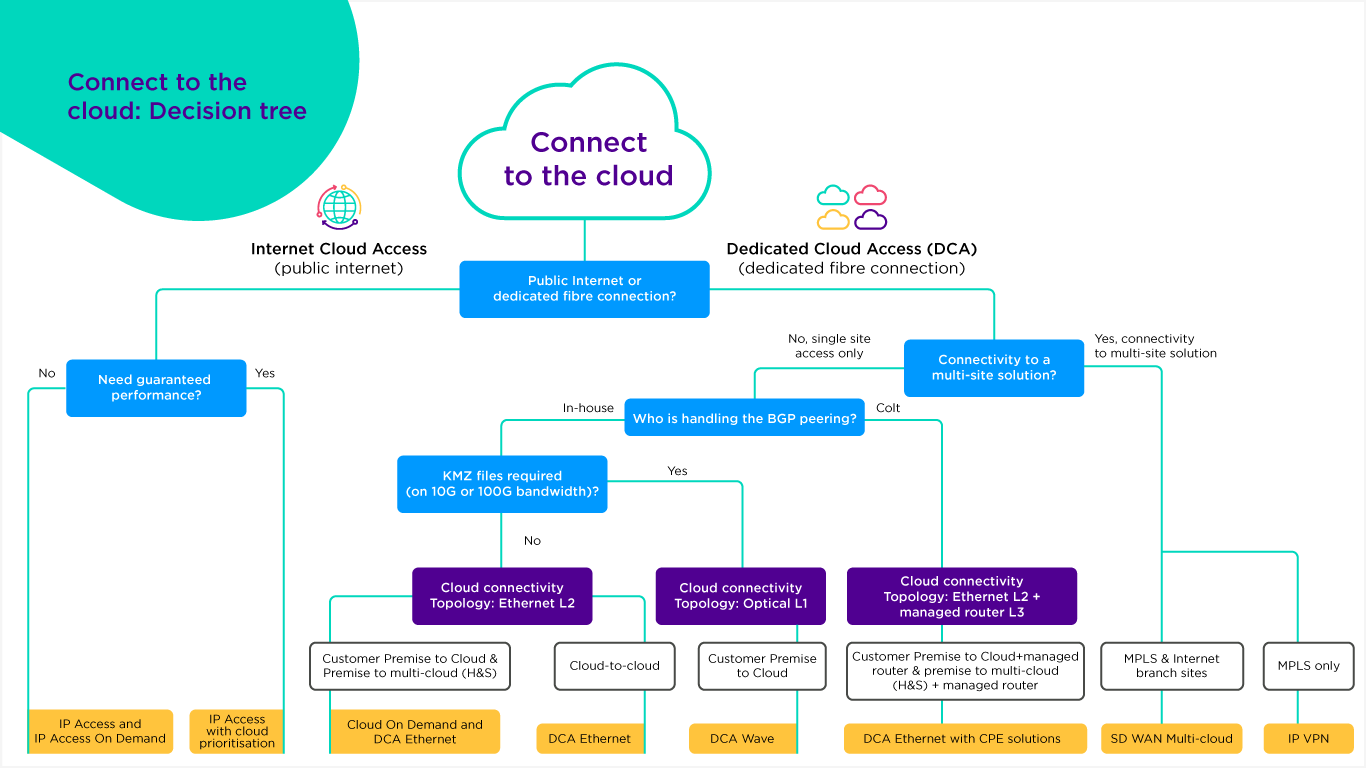
What solution is right for you?
Below is a high level Colt decision tree for cloud connectivity options for Colt's cloud connectivity portfolio offering.
(Click to expand)